Tutorial 4 – Three Scales of Potency
Today, homeopathic pharmacies utilize three potency scales for different prescribing purposes: the centesimal scale, the decimal scale, and the quinquagintamillesimal scale.
The Centesimal Scale
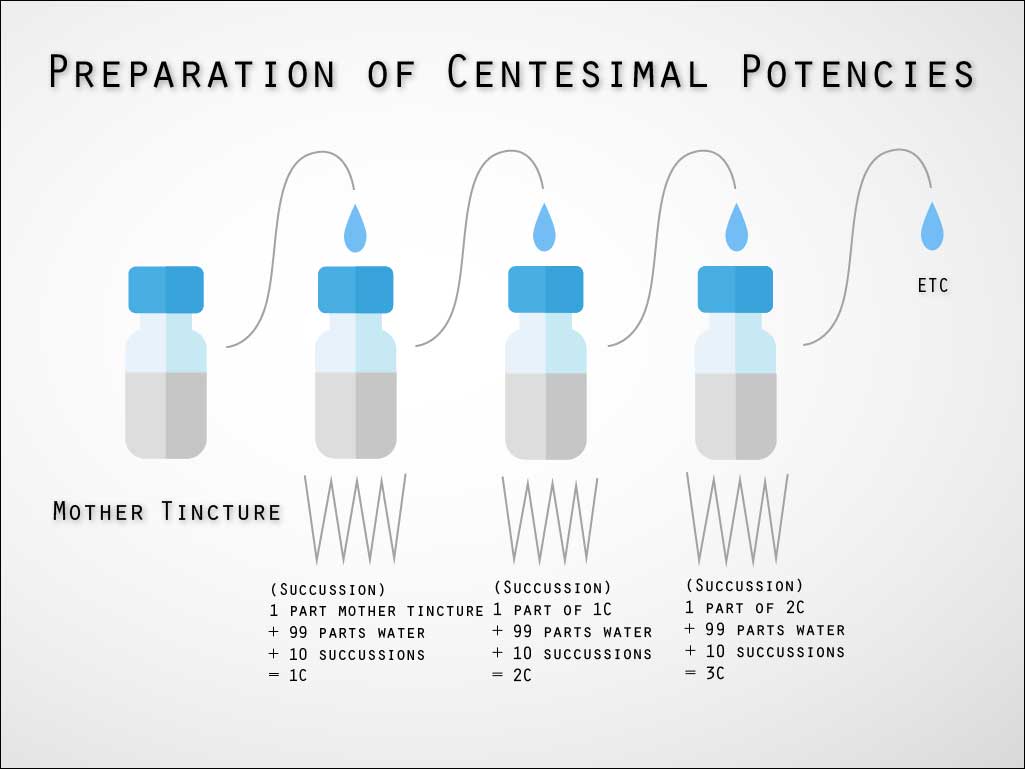
The centesimal scale, developed by Hahnemann in homeopathy’s early years, has a 1:100 dilution ratio. The process involves diluting one part of the mother tincture in 99 parts of a water-alcohol mixture, followed by succussion. This produces a 1C potency, with “C” representing the 1:100 dilution ratio. Serial dilution and succussion yield increasingly higher potencies. Centesimal remedies are versatile and suitable for treating acute and chronic diseases in various forms.
The Decimal Scale
The decimal scale, with a 1:10 dilution ratio, was the second potency scale in homeopathy’s development. One part of the mother tincture or potency is diluted in nine parts of a water-alcohol mixture, with ten succussions between each dilution phase. Decimal potencies are easy to use and can be administered in different forms, often used for self-treatment of simple acute problems.
The Quinquagintimillesimal Scale (Fifty Millesimal Scale)
The third scale, also known as fifty-millesimal, LM, or Q potencies, was developed shortly before Hahnemann’s death. With an initial dilution ratio of 1:50,000 and a more complex process than the centesimal and decimal scales, these potencies are deep-acting and flexible. They should only be dispensed as liquids and are typically reserved for practitioner use, as they require greater knowledge to prescribe appropriately.
Modern Potency Preparation
Pharmacies today prepare remedies using hand succussion or machines that mimic the process. Insoluble starting materials, such as metals, undergo grinding with lactose before being dissolved for potentisation. Each remedy is prepared in all three potency scales, allowing practitioners to choose the most suitable one for their patients. Homeopathic remedies become “sub-molecular” medicines free of chemical side effects after potentisation beyond 12C or 24X levels. Higher potency remedies generally act more deeply and induce longer-lasting reactions than lower potency counterparts.
Tutorials
- Homeopathy: an Introduction
- Tutorial 1 – The Law of Similars
- Tutorial 2 – Law of Similars Discovered
- Tutorial 3 – Potentisation
- Tutorial 4 – Three Scales of Potency
- Tutorial 5 – Benefits of Potentisation
- Tutorial 6 – Provings
- Tutorial 7 – The Vital Force
- Tutorial 8 – Potentised Remedies and the Vital Force
- Tutorial 9 – Palliation, Supression or Cure?
- Tutorial 10 – Direction of Cure
- Tutorial 11 – Return of Old Symptoms
- Tutorial 12 – Homeopathy and Other Medicinal Therapies
- Tutorial 13 – Finding a Good Homeopath
- Tutorial 14 – That First Appointment
- Tutorial 15 – What to Expect (Part A)
- Tutorial 16 – What to Expect (Part B)







